Buffer Reference Center
- pH Ranges of Selected Biological Buffers Chart (25 °C, 0.1 M)
- Tris or Trizma® Buffer Preparation – pH vs. Temperature
- Phosphate Buffer Preparation – 0.2 M solution
- Citric Acid – Na2HPO4 Buffer Preparation, pH 2.6-7.6
- Citric Acid – Sodium Citrate Buffer Preparation, pH 3.0-6.2
- Sodium Acetate – Acetic Acid Buffer Preparation, pH 3.7-5.6
- Na2HPO4 – NaH2PO4 Buffer Preparation, pH 5.8-8.0 at 25 °C
- Imidazole (glyoxaline) – HCl Buffer Preparation, pH 6.2-7.8 at 25 °C
- Sodium Carbonate – Sodium Bicarbonate Buffer Preparation, pH 9.2-10.8
- Buffer Preparation Formulas and Equations
Choosing the Right Biological Buffer
Choose a buffer based on your pH requirements as well as the pKa, a measure of acid strength that accounts for pH, concentration, and temperature. Regulatory or purity needs for your exact application should also be considered. The following tables can help you navigate preparation of many common buffer solutions by pH and pKa.
In addition to the tables below, we've developed several buffer recipe calculators to assist your buffer preparation.
TBE and TAE for gel electrophoresis have slightly more involved recipes. We can help you pick the right one.
What are buffer grades?
Buffer grade indicates the quality and impurity levels appropriate for different uses. We provide six grades of buffers indicated for general lab use, final pharmaceutical formulation and manufacturing, and applications in between that may need trace metal testing or materials of a specified purity.
Na2HPO4 – NaH2PO4 Buffer PREPARATION, pH 5.8-8.0 at 25 °C1
Na2HPO4 • 2H2O, MW 178.05; 0.2 M contains 35.61 g/L. Na2HPO4 • 12H2O, MW 358.22; 0.2 M contains 71.64 g/L. NaH2PO4 • H2O, MW 138.01; 0.2 M contains 27.6 g/L. NaH2PO4 • 2H2O, MW 156.03; 0.2 M contains 31.21 g/L.
x mL 0.2 M-Na2HPO4, y mL 0.2 M-NaH2PO4; diluted to 100 mL with H2O
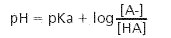
Reference
계속 읽으시려면 로그인하거나 계정을 생성하세요.
계정이 없으십니까?